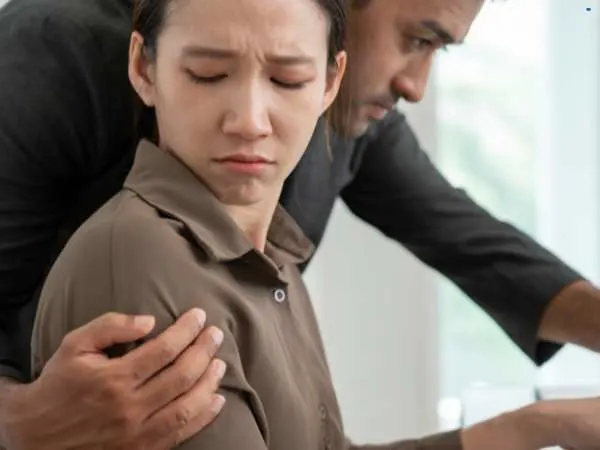
The phrase quid pro quo shows up everywhere. News headlines. Court cases. Office policies. Even casual talk. People use it when they mean “this for that,” but the phrase carries more weight than it first appears. It sounds formal. It sounds legal. It sounds serious. That’s because it is.
Understanding quid pro quo: the origins of the Latin term helps explain why it feels so loaded today. This isn’t just a catchy phrase. It comes from centuries-old language, evolved through law, economics, and power dynamics. Over time, its meaning narrowed in some areas and expanded in others.
This blog breaks it down slowly and clearly. Where the term came from. What it literally means. How pronunciation works. How it’s used in law, harassment cases, economics, and daily life. Each section gives context first, then examples, so nothing feels abstract.
Quid Pro Quo Meaning: What the Phrase Literally Says
At its core, quid pro quo meaning is simple. The phrase comes from Latin and translates to “something for something” or “this for that.” It describes an exchange where one thing is given with the expectation of receiving something in return.
Originally, the phrase did not carry moral judgment. It was descriptive, not accusatory. It simply named a transaction or substitution. Over time, English usage added emotional and ethical weight, especially in legal and workplace settings.
Key elements of the basic meaning:
- An exchange between two parties
- Each side gives something
- Each side expects something back
- The exchange may be spoken or implied
The meaning stays neutral until context changes it.
also read : – Elegant Last Name Ideas, Where They Come From, and Why Some Surnames Just Sound Refined
The Origins of Quid Pro Quo in Latin Usage
The origins of quid pro quo trace back to medieval Latin, not classical Roman literature as many assume. Early use appeared in medical and pharmaceutical writing, where it described substituting one ingredient for another.
In those texts, quid pro quo meant replacement, not bargaining. Apothecaries warned against swapping ingredients carelessly, as it could cause harm. That practical warning later moved into broader language.
Early usage focused on:
- Substitution
- Replacement of items
- Practical consequences
The phrase only later shifted toward exchange and obligation.
How Quid Pro Quo Entered English Language
Quid pro quo entered English around the 16th century. At first, it kept its substitution meaning. Writers used it to describe mistakes where one thing was confused for another.
Gradually, the phrase evolved. English speakers began using it to describe exchanges, favors, and implied deals. This shift happened naturally as trade, law, and social contracts became more formal.
Stages of change included:
- Medical substitution meaning
- Linguistic confusion or error
- Exchange or trade
- Conditional favor
Language drift changed how people heard the phrase.
Quid Pro Quo Pronunciation: How to Say It Correctly
Many people hesitate to say the phrase out loud. Quid pro quo pronunciation looks intimidating but is simple once broken down.
The standard pronunciation is:
- “kwid proh kwoh”
Each word is short and clipped. Stress stays even. Overpronouncing it often makes it sound unnatural.
Helpful tips:
- Say it smoothly, not dramatically
- Avoid adding extra syllables
- Keep the rhythm steady
Confidence matters more than accent.
Quid Pro Quo Examples in Everyday Life
Outside legal settings, quid pro quo shows up daily. People just don’t label it that way.
Everyday examples include:
- Helping a friend move in exchange for dinner
- Covering a shift expecting future help
- Trading favors between coworkers
These examples show that quid pro quo itself isn’t bad. It becomes an issue only when power imbalance or pressure enters the exchange.
also read : – How to Draw a Dragon (Simple Step-by-Step Guide)
Quid Pro Quo Meaning in Law: Why It Matters
Quid pro quo meaning in law carries serious consequences. In legal terms, it describes an explicit or implicit exchange tied to authority, power, or obligation. Courts care deeply about whether consent was free or coerced.
In law, quid pro quo often implies:
- Conditional benefit
- Abuse of authority
- Unequal power dynamics
That’s why it appears frequently in corruption and harassment cases.
Quid Pro Quo Harassment Meaning Explained Clearly
Quid pro quo harassment meaning refers to a specific form of workplace misconduct. It occurs when someone in authority demands something, often sexual, in exchange for job-related benefits or to avoid punishment.
This form of harassment does not require repetition. A single instance can qualify if the condition is clear.
Common features include:
- Power imbalance
- Conditional job benefit
- Pressure or threat
- Lack of true consent
This is why it’s treated seriously in workplace law.
Why Power Changes the Meaning of Quid Pro Quo
Power is the turning point. Without power imbalance, quid pro quo stays neutral. With power imbalance, it becomes coercive.
Power can come from:
- Job authority
- Control over grades
- Control over access or resources
When refusal carries consequences, the exchange stops being voluntary.
Quid Pro Quo Meaning in Law Versus Daily Speech
People often confuse casual use with legal meaning. In daily speech, quid pro quo might just mean fairness or balance. In law, it means something much stricter.
Differences include:
- Legal meaning requires authority
- Daily meaning allows mutual choice
- Legal meaning focuses on consent
Context defines interpretation.
Quid Pro Quo Examples in Workplace Settings
Workplace examples help clarify boundaries.
Examples that cross legal lines:
- Promotion offered for personal favors
- Threat of firing unless demands met
- Grades exchanged for non-academic benefits
Examples that do not:
- Negotiated salary increase for added duties
- Bonus tied to performance metrics
Intent and power matter.
also read :- How Long Is Hamburger Good in the Fridge? A Practical Guide You’ll Actually Use
Quid Pro Quo in Economics: A Neutral Exchange
Quid pro quo in economics returns the phrase closer to its original neutrality. In economics, it simply describes exchange relationships where value moves both ways.
Markets rely on quid pro quo:
- Goods exchanged for money
- Labor exchanged for wages
- Services exchanged for fees
Here, the term carries no moral weight. It describes structure, not abuse.
Why Economics Uses the Term Differently
Economics assumes voluntary participation. Each party agrees freely. No hidden threat exists.
Economic quid pro quo depends on:
- Informed choice
- Equal opportunity to refuse
- Transparent terms
Once coercion enters, economics gives way to ethics and law.
Quid Pro Quo and Corruption Allegations
In politics and public office, quid pro quo raises alarms. It suggests officials traded public power for private gain.
Examples include:
- Policy favors for donations
- Contracts exchanged for influence
- Access sold for loyalty
Here, the phrase implies betrayal of public trust.
How Media Changed Public Perception of Quid Pro Quo
Media coverage shaped modern understanding. Headlines often frame quid pro quo as inherently bad. Over time, this overshadowed its neutral origins.
As a result:
- The phrase now signals scandal
- Context gets lost
- Public reaction becomes emotional
Language evolves with culture.
Why People Misuse the Term Quid Pro Quo
Many people use quid pro quo incorrectly. They apply it to any exchange, even harmless ones.
Common misuse includes:
- Calling normal negotiation unethical
- Confusing mutual agreement with coercion
- Ignoring power differences
Precision matters when language carries legal weight.
How to Use Quid Pro Quo Correctly in Writing
Writers should use the term carefully. Overuse weakens meaning.
Best practices include:
- Define context clearly
- Clarify power dynamics
- Avoid sensational tone
Accuracy builds credibility.
also read : – Difference between March VS February Pisces
Psychological Impact of Quid Pro Quo Situations
In coercive settings, quid pro quo creates lasting stress. People feel trapped, blamed, or confused.
Psychological effects may include:
- Anxiety
- Loss of trust
- Shame
- Reduced self-worth
This explains why laws address it directly.
Cultural Differences in Understanding Quid Pro Quo
Different cultures view exchange differently. Some see favor exchange as normal social bonding. Others see it as suspicious.
Cultural factors include:
- Hierarchy norms
- Gift-giving traditions
- Workplace structure
Context shapes interpretation.
Why the Term Still Matters Today
Despite its age, quid pro quo remains relevant. It captures a universal concept: exchange with expectation. As systems grow complex, naming that dynamic helps regulate behavior.
Its value lies in clarity.
Common Myths About Quid Pro Quo
Several myths confuse people.
Common myths include:
- All quid pro quo is illegal
- Quid pro quo always involves sex
- Any favor exchange qualifies
None of these are universally true.
FAQs
What is quid pro quo meaning
It means “this for that,” describing an exchange.
What is quid pro quo harassment meaning
It refers to conditional demands tied to power, often in workplaces.
What is quid pro quo meaning in law
A conditional exchange involving authority or coercion.
How do you pronounce quid pro quo
It is pronounced “kwid proh kwoh.”
What is quid pro quo in economics
A neutral exchange of value between parties.
Final Words
Quid pro quo began as a practical Latin phrase about substitution. Over centuries, it evolved into a powerful term tied to law, ethics, and authority. Its meaning shifts with context. Sometimes neutral. Sometimes dangerous. Always dependent on power and consent.
Knowing its origins helps cut through confusion. When you understand where the term came from and how it’s used today, you can recognize when it describes fairness and when it signals abuse. Language matters. And few phrases show that more clearly than quid pro quo.